Horii T, Morita S, Kimura M, Hatada I (IMCR, Gunma Univ.) Yamamoto M (Advanced Scientific Research Leaders Development Unit, Gunma Univ.) Nagao Y (Jichi Medical Univ.)
About
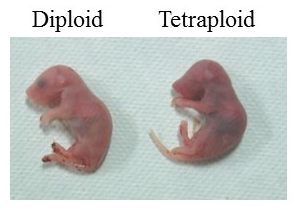
Mammalian tetraploid embryos die in early development because of defects in the epiblast. Experiments with diploid/tetraploid chimeric mice, obtained via the aggregation of embryonic stem cells, clarified that while tetraploid cells are excluded from epiblast derivatives, diploid embryos with tetraploid extraembryonic tissues can develop to term. Today, this method, known as tetraploid complementation, is usually used for rescuing extraembryonic defects or for obtaining completely embryonic stem (ES) cell-derived pups. However, it is still unknown why defects occur in the epiblast during mammalian development. Here, we demonstrated that downregulation of p53, a tumour suppressor protein, rescued tetraploid development in the mammalian epiblast. Tetraploidy in differentiating epiblast cells triggered p53-dependent apoptosis, suggesting the activation of a tetraploidy checkpoint during early development. Finally, we found that p53 downregulation rescued tetraploid embryos later in gestation.
Paper information
p53 Suppresses Tetraploid Development in Mice.
Horii T, Yamamoto M, Morita S, Kimura M, Nagao Y, Hatada I.
Scientific Reports, 5:8907, 2015
Online URL
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25752699
Lab HP
http://epigenome.dept.showa.gunma-u.ac.jp/~hatada/index.php?id=63