Kunli Zhao, Kohichi Matsunaga, Kouichi Mizuno, Hao Wang, Katsuhide Okunishi, and Tetsuro Izumi* (Laboratory of Molecular Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Molecular Medicine, Institute for Molecular and Cellular Regulation, Gunma University, Maebashi 371-8512, Japan *: Corresponding author)
About
The Rab27 effectors are known to play versatile roles in regulated exocytosis. In pancreatic beta cells, exophilin-8 anchors granules in the peripheral actin cortex, whereas granuphilin and melanophilin mediate granule fusion with and without stable docking to the plasma membrane, respectively. However, it is unknown whether these coexisting effectors function in parallel or in sequence to support the whole insulin secretory process. Here, we investigate their functional relationships by comparing the exocytic phenotypes in mouse beta cells simultaneously lacking two effectors with those lacking just one of them. Analyses of prefusion profiles by total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy suggest that melanophilin exclusively functions downstream of exophilin-8 to mobilize granules for fusion from the actin network to the plasma membrane after stimulation. The two effectors are physically linked via the exocyst complex. Downregulation of the exocyst component affects granule exocytosis only in the presence of exophilin-8. The exocyst and exophilin-8 also promote fusion of granules residing beneath the plasma membrane prior to stimulation, although they differentially act on freely diffusible granules and those stably docked to the plasma membrane by granuphilin, respectively. The present study is the first to diagram the multiple intracellular pathways of granule exocytosis and the functional hierarchy among different Rab27 effectors within the same cell.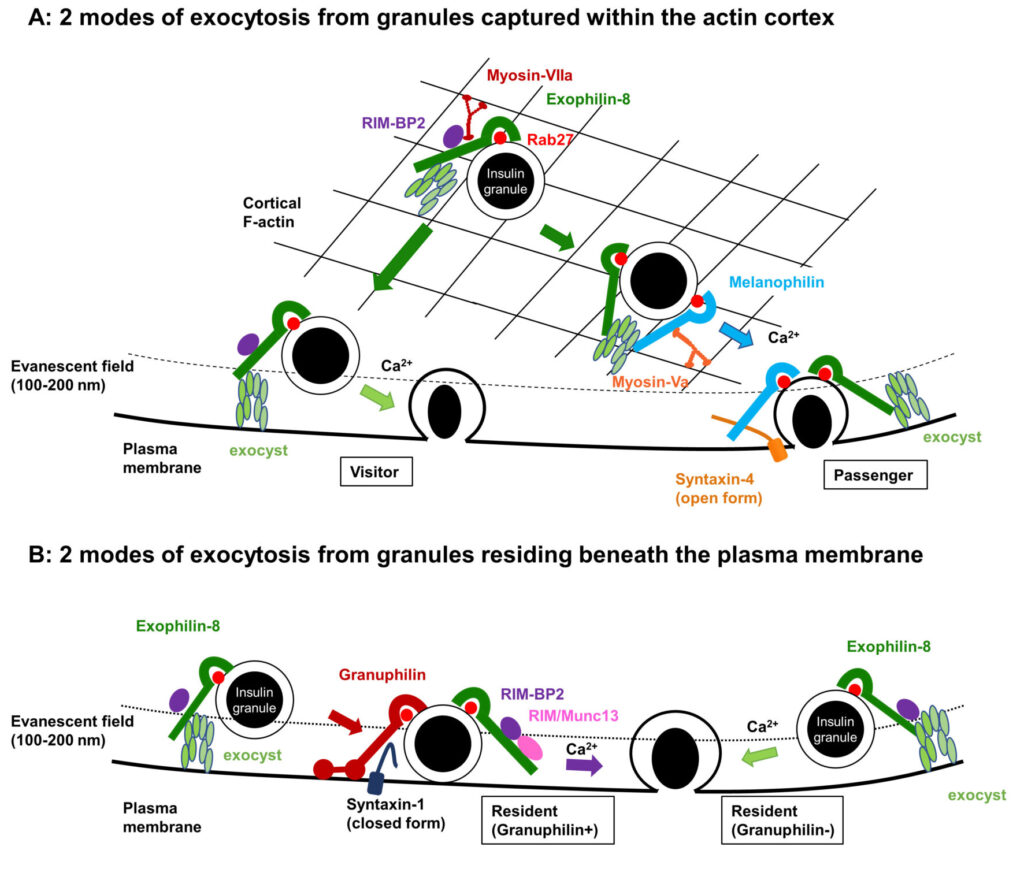
Paper information
Functional hierarchy among different Rab27 effectors involved in secretory granule exocytosis
Elife 2023 Feb 21;12:e82821. doi: 10.7554/eLife 82821. PMID: 36803984
Online URL
https://elifesciences.org/articles/82821