Saegusa K, Sato K (Lab. Mol. Traffic, IMCR, Gunma Univ.) Sato M, Sato K (Lab. Mol. Memb. Biol., IMCR, Gunma Univ.) Nakajima-Shimada J (School of Health Sciences, Gunma Univ.) Harada A (Osaka Univ.)
About
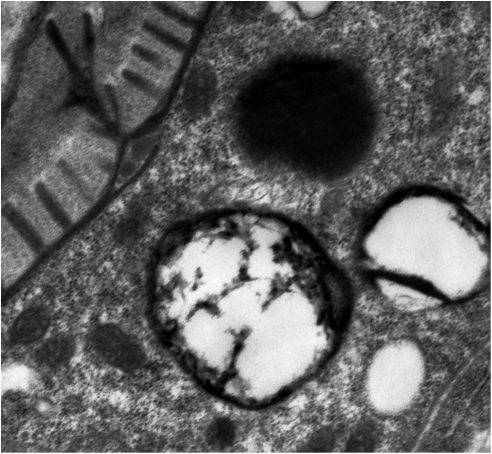
Intestinal epithelial cells have unique apical membrane structures, known as microvilli, that contain bundles of actin microfilaments. In this study, we report that Caenorhabditis elegans cytosolic chaperonin containing TCP-1 (CCT) is essential for proper formation of microvilli in intestinal cells. In intestinal cells of cct-5(RNAi) animals, a substantial amount of actin is lost from the apical area, forming large aggregates in the cytoplasm, and the apical membrane is deformed into abnormal, bubble-like structures. The length of the intestinal microvilli is decreased in these animals. However, the overall actin protein levels remain relatively unchanged when CCT is depleted. We also found that CCT depletion causes a reduction in the tubulin levels and disorganization of the microtubule network. In contrast, the stability and localization of intermediate filament protein IFB-2, which forms a dense filamentous network underneath the apical surface, appears to be superficially normal in CCT-deficient cells, suggesting substrate specificity of CCT in the folding of filamentous cytoskeletons in vivo. Our findings demonstrate physiological functions of CCT in epithelial cell morphogenesis using whole animals.
Paper information
C. elegans chaperonin CCT/TRiC is required for actin and tubulin biogenesis and microvillus formation in intestinal epithelial cells.
Saegusa K, Sato M, Sato K, Nakajima-Shimada J, Harada A*, Sato K*
Mol Biol Cell 15; 25(20):3095-104, 2014
Online URL
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25143409