Akihito Morita1,2) *, Yuhkoh Satouh1) *, Hidetaka Kosako3), Hisae Kobayashi1), Akira Iwase2), and Ken Sato1) ‡ 1. Laboratory of Molecular Traffic, Institute for Molecular and Cellular Regulation, Gunma University, Maebashi, Japan. 2. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Gunma University Graduate School of Medicine, Maebashi, Japan 3. Fujii Memorial Institute of Medical Sciences, Institute of Advanced Medical Sciences, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan
About
In the present study, we have clarified the mechanism underlying how maternal plasma membrane proteins are selectively internalized and degraded in embryos and identified its physiological role in mammalian early embryonic development.
The fertilization triggers drastic cellular remodeling through the oocyte-to-embryo transition for appropriate development. However, it has been unclear how the maternal plasma membrane proteins are sorted and degraded during early development. In this study, we found that multiple maternal plasma membrane proteins such as GlyT1a, which is a glycine transporter dominantly expressing on mouse embryos, are selectively internalized via endocytosis by the late two-cell stage and degraded in lysosomes. We also revealed the involvement of protein ubiquitination in the selective degradation of such maternal plasma membrane proteins. Finally, we showed that Protein Kinase C (PKC)-dependent clathrin-mediated endocytosis is essential for the selective degradation of maternal membrane proteins during oocyte-to-embryo transition and thereby for early embryogenesis.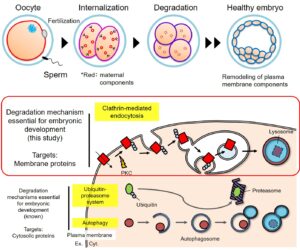
Paper information
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is essential for the selective degradation of maternal membrane proteins and preimplantation development.
Morita A, Satouh Y, Kosako H, Kobayashi H, Iwase A, Sato K.
Development. 2021 Jul 15;148(14):dev199461. doi: 10.1242/dev.199461. Epub 2021 Jul 16. PMID: 34269385
Online URL
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34269385/