Professor : INAGAKI Takeshi
inagaki*gunma-u.ac.jp
(*=@)
Lab website
http://epigenetics.imcr.gunma-u.ac.jp/
Member
Professor: INAGAKI Takeshi
Associate Professor: KOMATSU Tetsuro
Assistant Professor: SUZUKI Tomohiro
Postdoctoral Fellow: WANG Shuai
Postdoctoral Fellow: KATO Taku
Resercher: HAYASHI Mayuko
Resercher: Safiya ATIA
Technical Assistant: TANIOKA Akiko
Technical Assistant: Sucharita SENGUPTA
Technical Assistant: ODAGIRI Mayumi
Technical Assistant: SUGA Emi
Graduate Student: AHAMED MOHAMMAD SELIM
Graduate Student: YU Hai
Graduate Student: HASAN TAREK
Graduate Student: Ninghang ZHU
Graduate Student: KHATUN SUMI MIRA
Research
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression is independent of genomic sequence and therefore can flexibly respond to environmental factors. We are currently investigating various epigenetic mechanisms by which the environmental factors are linked to metabolic diseases. Main focus of our research is histone modification which regulates gene expression through changing chromatin structure and cofactor recruitment. Using techniques of transcriptomics, epigenetics, proteomics and animal models, we intend to elucidate the detail mechanisms of epigenetic regulations of energy metabolism and adipose cell development.
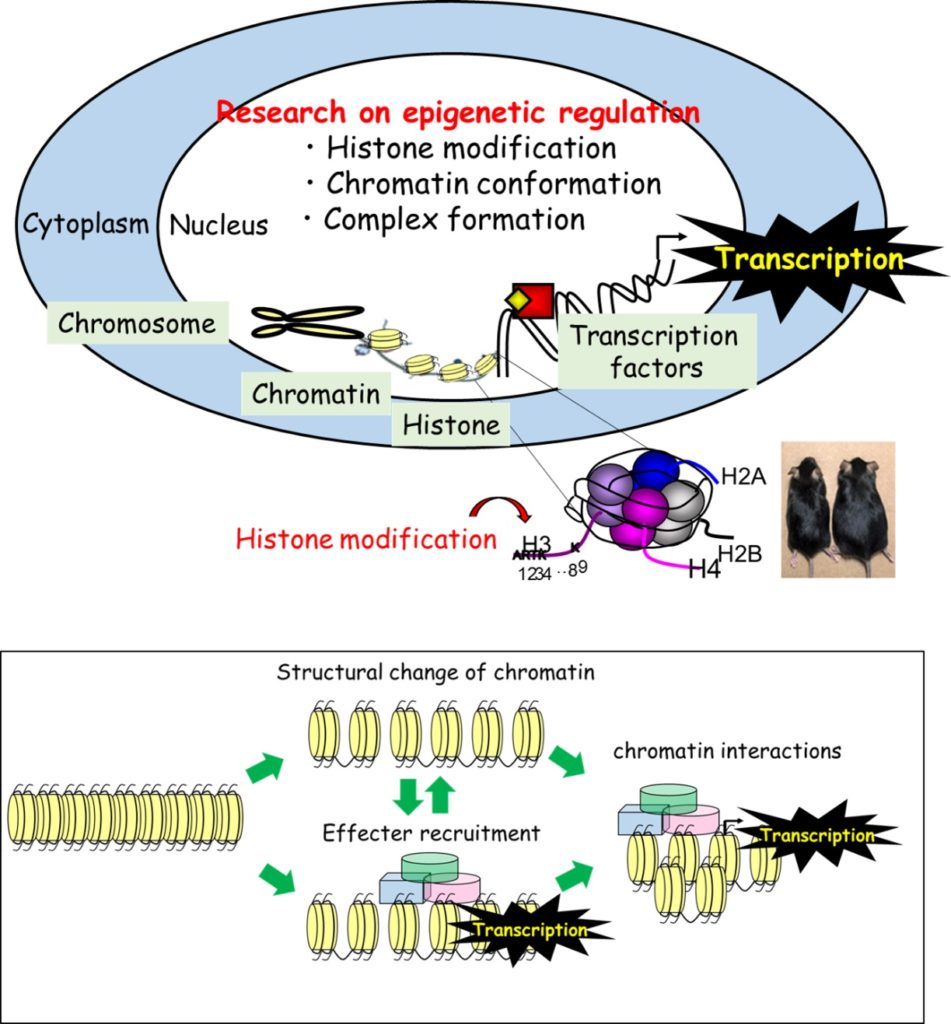
On-going projects
- Investigation of transcriptional regulation mechanisms regulated by histone demethylases
- Elucidation of epigenetics in adipocyte differentiation and trans-differentiation
- Comprehensive analysis of histone codes
- Nuclear receptors and endocrine fibroblast growth factors
Keywords
Epigenome, metabolic diseases, energy metabolism, transcription, chromatin structure
Select References
- Suzuki T et al. (2023). Nucleic Acids Research 51;12;6120-6142
- Abe Y. et al. (2018). Nature Communications 19;9(1):1556
- Inagaki T. et al. (2016). Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 17(8):480-95
- Abe Y. et al. (2015). Nature Communications 7;6:7052
- Inagaki T. et al. (2009). Genes to Cells 14(8):991-1001
- Inagaki T. et al. (2007). Cell Metabolism 5(6), 415-425
- Inagaki T. et al. (2005). Cell Metabolism 2(4), 217-225