Professor: KITAMURA Tadahiro
kitamura*gunma-u.ac.jp
(*=@)
Lab website
http://taisha.imcr.gunma-u.ac.jp/index.html
Member
Professor: KITAMURA Tadahiro
Associate Professor: KOBAYASHI Masaki
Assistant Professor: KOHNO Daisuke
Research Associate: HASHIMOTO Hiromi
Postdoctoral Fellow: KIKUCHI Osamu
Technical Assistant: SUZUKI Hiroko
Graduate Student: IKEUCHI Yuichi
Graduate Student: TABEI Youko
Graduate Student: YOSHIKAWA Chiharu
Undergraduate student : OTANI Kurumi
Collaborative Researcher: SUGA Takayoshi
Research
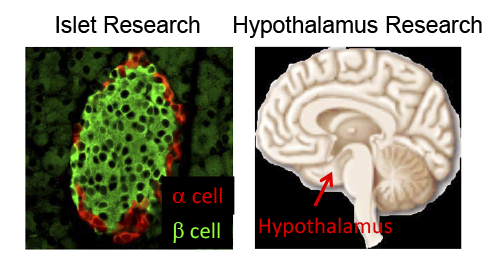
It is considered that type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is caused by insulin resistance (loss of insulin function) and pancreatic beta cell failure (loss of insulin secretion). However, recent genetic studies using molecular biology and gene manipulating technology revealed that pancreatic alpha cell (secreting glucagon) failure and the dysfunction of central energy metabolism also account for the etiology of T2DM. Therefore, we are conducting research by using animal models of diabetes with focusing on the pancreatic islets and the hypothalamus. We are attempting to clarify the molecular mechanism of T2DM and apply it to the development of new strategy to treat or prevent diabetes
On-going projects
- Clarifying the molecular mechanism of pancreatic beta cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes
- Elucidating how “metabolic signals” regulate energy homeostasis in the hypothalamus at the molecular level
- Investigating the molecular mechanism by which plasma glucagon levels elevate in type 2 diabetes
- Developing a new glucagon sandwich ELISA system and re-evaluating plasma glucagon levels
- Investigating molecular mechanism for the extra beneficial effects of anti-diabetes drugs toward controlling body weight and glucagon secretion
Keywords
Diabetes, Obesity, Insulin, Glucagon, Genetically engineered animal model, Pancreatic cell, Pancreatic β cell, Hypothalamus, Metabolism, Life span
Select References
- Ariyani W.et al.(2025) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 122:e2411069122.
- Kobayashi M.et al.(2023) J Diabetes Investig 14:648-658.
- Wada E. et al. (2021) J Nutri Biochem 97:108811.
- Kobayashi M. et al. (2021) J Diabetes Investig 12: 286-289.
- Kobayashi M. et al. (2020) Endocr J 67: 903-922.
- Suga T. et al. (2019) Mol Metab.19:1-12.
- Matsui S. et al. (2018) Nat Communi 9: 4604-4620.
- Miyachi A. et al. (2017) Anal Bioanal Chem 409: 5911-5918.
- Kitamura T. (2013) Nat Rev Endo 9: 615-23.