Ryota Inoue 1,2 Takahiro Tsuno 1,2 Yu Togashi 2 Tomoko Okuyama 2 Aoi Sato 1 Kuniyuki Nishiyama 1,2 Mayu Kyohara 2 Jinghe Li 1,2 Setsuko Fukushima 1 Tatsuya Kin 3 Daisuke Miyashita 2 Yusuke Shiba 2 Yoshitoshi Atobe 4 Hiroshi Kiyonari 5 Kana Bando 5 A. M. James Shapiro 3 Kengo Funakoshi 4 Rohit N. Kulkarni 6 Yasuo Terauchi 2 and Jun Shirakawa 1,2* (1. Laboratory of Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders, Institute for Molecular and Cellular Regulation (IMCR), Gunma University, Maebashi 371-8512, Japan. 2. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Graduate School of Medicine, Yokohama City University, Yokohama 236-0004, Japan. 3. Clinical Islet Laboratory and Clinical Islet Transplant Program, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB T6G2C8, Canada. 4. Department of Neuroanatomy, Yokohama City University School of Medicine, Yokohama 236-0004, Japan. 5. Laboratory for Animal Resources and Genetic Engineering, RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research, Kobe 650-0047, Japan. 6. Islet Cell and Regenerative Biology, Joslin Diabetes Center, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Stem Cell Institute, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02215, USA.; *, Corresponding Author)
About
In this study, we have provided an evidence that UCP2 and AldB play a role in key pathological processes of type 2 diabetes. We investigated the significance of the increase in UCP2 expression in islets from type 2 diabetes, using human islets and β-cell-specific UCP2-overexpressing transgenic mice (βUCP2Tg). βUCP2Tg showed glucose intolerance with reduced insulin secretion. Overexpression of UCP2 induced mitochondrial dysfunction and impairment of Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in β-cells. Aldolase B (AldB), a glycolytic enzyme, was highly expressed in βUCP2Tg islets and associated with reduced insulin secretion via mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired Ca2+ release from the ER. Taken together, we discovered the novel mechanism that UCP2 in stressed β-cells under diabetes decreased insulin secretion due to mitochondrial dysfunction and impairment of Ca2+ release from the ER by inducing AldB expression. Targeting the UCP2/AldB axis is a promising approach for the recovery of β-cell function.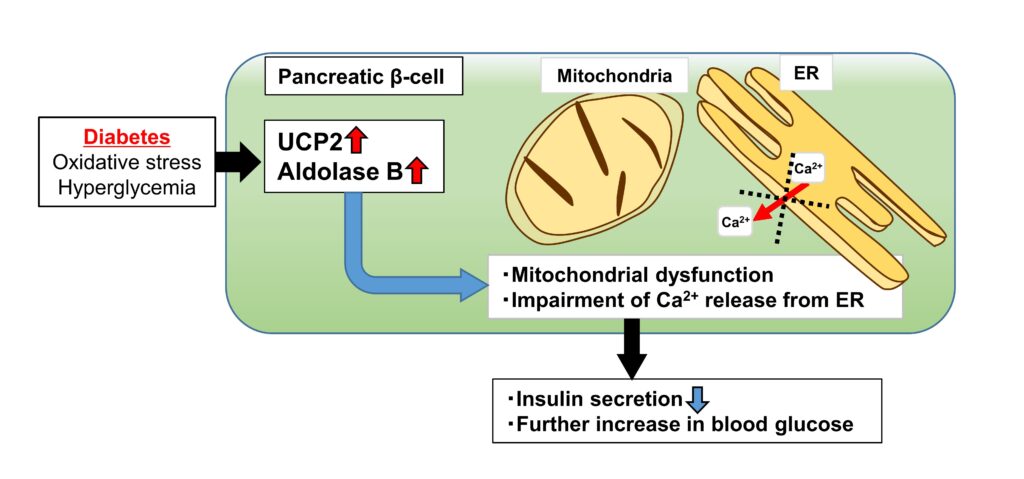
Paper information
Uncoupling protein 2 and aldolase B impact insulin release by modulating mitochondrial function and Ca2+ release from the ER” iScience誌(Cell Press)
Online URL
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35800776/