Kato M, Shimizu A, Yokoyama, Y, Ishikawa O (Dept. of Dermatol., Gunma Univ. Grad. Sch. of Med.) Kamei K, Tokunaga F (IMCR, Gunma Univ.) Kaira K (Dept. of Oncol. Clin. Develop., Gunma Univ. Grad. Sch. of Med.) Shimomura Y (Lab. of Genetic Skin Dis., Niigata Univ. Grad. Sch. of Medical and Dental Sci.) Ishida-Yamamoto A (Dept. of Dermatol., Asahikawa Medical Univ.)
About
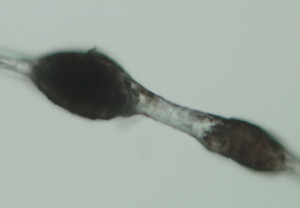
We identified a novel mutation in the desmoglein 4 (DSG4) gene from an autosomal recessive monilethrix patient. Observation of her hair shaft by means of transmission electron microscopy showed fewer desmosomes and abnormal keratinization. In the patient’s hair shaft, we detected reduced but partial expression of the mutant DSG4 protein. The amounts of mutant DSG4 were increased by proteasome inhibitor treatment, and the expression of an ER chaperone, GRP78/BiP, was elevated in the patient’s skin. Collectively, these results suggest that the dysfunctional mutated DSG4, and thus ER stress may have a role in the pathogenesis of monilethrix.
Paper information
A novel autosomal recessive mutation of DSG4 causes monilethrix through the ER stress response.
Kato M, Shimizu A, Yokoyama Y, Kaira K, Shimomura Y, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Kamei K, Tokunaga F, Ishikawa O.
J Invest Dermatol 135(5): 1253-60, 2015
Online URL
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25615553