Matsunaga K1, Taoka M2, Isobe T2, Izumi T1 (1 Laboratory of Molecular Endocrinology and Metabolism, IMCR、Gunma University, 2Laboratory of biophysics and biochemistry, Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Tokyo Metropolitan University)
About
Secretion of insulin requires a series of membrane dynamics, namely, producing granules from the Golgi apparatus, sorting and maturation of cargo proteins, and trafficking and fusion to the plasma membrane. Previous studies reported that Rab27a small GTPase regulates the series of insulin granule trafficking and exocytosis through its multiple effector proteins. Although the molecular machinery for these individual processes has been characterized, the precise mechanisms linking each process remain poorly understood. In this study, we report that Noc2, a well-known Rab27a effector, also bound to another small GTPase Rab2a in GTP dependent manner. The ternary Rab27a-Noc2-Rab2a complex was specifically localized to immature proinsulin granules, whereas the binary Rab27a-Noc2 complex was localized to mature insulin granules. Moreover, siRNA gene silencing experiments revealed that the ternary complex functioned in granule maturation, whereas the binary complex functioned in granule trafficking and secretion. The present study provides evidence that Noc2 functions as a dual effector for Rab27a and Rab2a and regulates transition from granule maturation to exocytosis in the insulin secretion pathway.
The dual effector, Noc2, regulates transition from Rab2a-mediated granule biogenesis to Rab27a-mediated granule exocytosis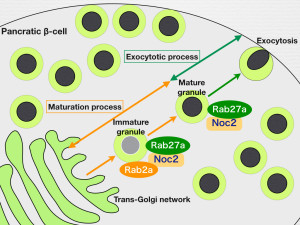
Paper information
Matsunaga K, Taoka M, Isobe T, Izumi T (2017). Rab2a and Rab27a cooperatively regulate transition from granule maturation to exocytosis through the dual effector Noc2. J Cell Sci., 130, 541-550 doi:10.1242/jcs.195479. PMID: 27927751
Online URL
http://jcs.biologists.org/content/130/3/541