Sumiyo Morita1, Hirofumi Noguchi2#, Takuro Horii1#, Kazuhiko Nakabayashi3, Mika Kimura1, Kohji Okamura4, Atsuhiko Sakai2, Hideyuki Nakashima2, Kenichiro Hata3, Kinichi Nakashima2, and Izuho Hatada1* 1. Institute for Molecular and Cellular Regulation, Gunma University, Maebashi, Japan 2. Department of Stem Cell Biology and Medicine, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan 3. Department of Maternal-Fetal Biology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development, Tokyo, Japan 4. Department of Systems BioMedicine, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development, Tokyo, Japan About *Corresponding author: E-mail: hatada@gunma-u.ac.jp # These authors contributed equally to this work.
About
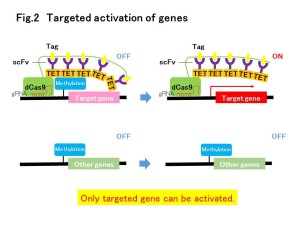
Despite the importance of DNA methylation in health and disease, technologies to readily manipulate methylation of specific sequences for functional analysis and therapeutic purposes are lacking. Here we adapt the previously described dCas9–SunTag for efficient, targeted demethylation of specific DNA loci. The original SunTag consists of ten copies of the GCN4 peptide separated by 5-amino-acid linkers. To achieve efficient recruitment of an anti-GCN4 scFv fused to the teneleven (TET) 1 hydroxylase, which induces demethylation,we changed the linker length to 22 amino acids. The system attains demethylation efficiencies >50% in seven out of nine loci tested. Four of these seven loci showed demethylation of >90%. We demonstrate targeted demethylation of CpGs in regulatory regions and demethylation-dependent 1.7- to 50-fold upregulation of associated genes both in cell culture (embryonic stem cells, cancer cell lines, primary neural precursor cells) and in vivo in mouse fetuses.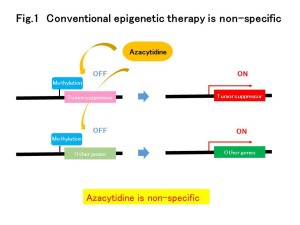
Paper information
Sumiyo Morita, Hirofumi Noguchi, Takuro Horii, Kazuhiko Nakabayashi, Mika Kimura, Kohji Okamura, Atsuhiko Sakai, Hideyuki Nakashima, Kenichiro Hata, Kinichi Nakashima, and Izuho Hatada.Targeted DNA demethylation in vivo using dCas9-peptide repeat and ScFv–TET catalytic domain fusions
Nature Biotechnology 2016 Online issue(29, August 2016, 11:00:00EDT 30, August 2016, 00:00:00JST)DOI:10.1038/nbt.3658
Online URL
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27571369